
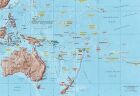
 The islands are located between the subtropical latitudes of North. (28 ° 25 ' N) and South temperate latitudes. (52 ° 30 ' S) hemispheres; most of them h. divided into arch. submeridional. Total Space. Islands 1.6 million. km2; OK. 9 million. Pers. The largest of the islands - New Guinea Islands and the North and South that make up New Zealand - occupy 80 % of the entire territory of O. When splitting the globe in hours. Light O. usually combined with Australia. Oceania name came into use in the beginning of the XIX century. In 1832, explorer Dumont d'Urville proposed division of the Islands into three major parts .: Polynesia, Micronesia and Melanesia. About Islands app. Micronesia, Melanesia and New Zealand are mountainous and heavily dissected. The mountain ranges are reaching a great height; O. highest point - city Jaya to Papua New Guinea (5029 m). In the center. h. from the depths of the Pacific Ocean seabed rising giant basalt cones crowning volcanic ridges; their surface peaks - the highest volcanoes of Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea on the island. Hawaii. Among the volcanic Islands are: Hawaii, Samoa, Marquesas, Society, Cook (Southern), Austral Islands, about. Easter and others. Smaller; active volcanism characteristic of New Zealand. On the eastern islands. Micronesia and Polynesia - small, low coral atolls rarely mountainous, b. h. low. Except for a few volcanic Islands in DOS. coral are groups of islands: Marshall, Caroline, Gilbert, Ellis, Tokelau, Cook (North.), Phoenix, Line, Tuamotu, Nauru and others. smaller. There are large deposits of nickel (New Caledonia), phosphates (Nauru), oil (New Guinea), gold (Papua - New Guinea), Cam. coal (New Zealand), copper (about. Bougainvillea) and others.
The islands are located between the subtropical latitudes of North. (28 ° 25 ' N) and South temperate latitudes. (52 ° 30 ' S) hemispheres; most of them h. divided into arch. submeridional. Total Space. Islands 1.6 million. km2; OK. 9 million. Pers. The largest of the islands - New Guinea Islands and the North and South that make up New Zealand - occupy 80 % of the entire territory of O. When splitting the globe in hours. Light O. usually combined with Australia. Oceania name came into use in the beginning of the XIX century. In 1832, explorer Dumont d'Urville proposed division of the Islands into three major parts .: Polynesia, Micronesia and Melanesia. About Islands app. Micronesia, Melanesia and New Zealand are mountainous and heavily dissected. The mountain ranges are reaching a great height; O. highest point - city Jaya to Papua New Guinea (5029 m). In the center. h. from the depths of the Pacific Ocean seabed rising giant basalt cones crowning volcanic ridges; their surface peaks - the highest volcanoes of Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea on the island. Hawaii. Among the volcanic Islands are: Hawaii, Samoa, Marquesas, Society, Cook (Southern), Austral Islands, about. Easter and others. Smaller; active volcanism characteristic of New Zealand. On the eastern islands. Micronesia and Polynesia - small, low coral atolls rarely mountainous, b. h. low. Except for a few volcanic Islands in DOS. coral are groups of islands: Marshall, Caroline, Gilbert, Ellis, Tokelau, Cook (North.), Phoenix, Line, Tuamotu, Nauru and others. smaller. There are large deposits of nickel (New Caledonia), phosphates (Nauru), oil (New Guinea), gold (Papua - New Guinea), Cam. coal (New Zealand), copper (about. Bougainvillea) and others. The climate is oceanic, constantly moist, preim. equatorial and sub-equatorial in the south subtropical and temperate. In the equatorial belt Wed-months. so-ture throughout the year 26-28 ° C, in the extreme south of 16 ° C in February and 5 ° C in August. Rainfall from 1000 mm in the east to 3,000-4,000 mm in the west especially a lot of them falls on the windward slopes of mountainous Islands (the Hawaiian Islands in some places more than 10 000 mm). Glaciers are found in the mountains of New Guinea and the South Island of New Zealand. On the windward slopes of mountainous Islands is dominated by moist evergreen forests, and on the lee - xerophytic hard-leaved forests and shrubs. There are areas of vegetation such as savannas. On ism. Coral Islands - bushes, forest areas, groves of coconut palms, breadfruit, and others. The fauna is poor; very small mammals and many insects and birds. There are endemic; for example, only on the islands of New Guinea and New Britain are known cassowaries.
Home European Open Oceania in 1521 put the expedition F. Magellan, who crossed the Pacific Ocean trade winds in the band and found Mariana Islands. In the 1528-29 biennium. Spaniard A. Saavedra discovered the Marshall and Caroline Islands, in 1568 his countryman A. Mendaña de Neira discovered the Solomon Islands, and in the re-sail in 1595 - the Marquesas Islands and the architect. Santa Cruz. In the 1642-43 biennium. Dutch navigator A. Tasman discovered Tasmania, New Zealand, Tonga Islands and Fiji, 1699-1700 gg. Englishman William Dampier - Islands north of New Guinea, in 1772, the Dutchman J. Roggeveen - a. Easter Islands and Samoa. In 1767 an Englishman S. Wallis discovered about. Tahiti, a year later the French navigator LA Bougainville - a number of islands of Melanesia. Englishman George. Cook in his three voyages (1768-79) thoroughly examined New Zealand, discovered a number of islands in the arch. Society, Tuamotu, New Hebrides, on. New Caledonia and the Hawaiian Islands. In the XIX century. major contribution to the discovery and study of OA made Russian sailors IF Kruzenshtern, Y. Lisyansky, OE Kotzebue, VM Golovnin, FF Bellingshausen, MP Lazarev, F. P . Litke, N. Maclay et al.
Oceania inhabited by many nations, very different racial, linguistic, historical and cult. relations. Roughly equal proportions are now living natives and newcomers. Indigenous peoples belong to the Polynesian, Melanesian and Micronesian anthropological types. Ch locals speak the Malayo-Polynesian languages, etc. H. To r. N. Papuan languages. Since the beginning of the XIX century. Most of the islands have been turned into Oceania colonies of European powers: Britain, France, Portugal, Germany and others. Since the beginning of the 1960s, many of the former colonies gained their independence OA.
Geographical position
It is the largest of the spatial coverage of the region, the accumulation of more than 10 thousand. Islands in the Pacific Ocean. The area of territory - 9 million sq. M. km, including the area of Australia - 7.7 million sq. m. km. Oceania is divided into 3 parts: Melanesia - the south-western part of the ocean where there are 4 sovereign states (Papua - New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu and Fiji), Micronesia - the north-western part of the ocean, where the three sovereign states (Federated States of Micronesia Marshal-catches Islands and Palau), Polynesia, stretching in Merida-functional direction in the central part of the ocean where the focus 6 countries (New Zealand, Samoa, Kiribati, Nauru, Tonga, Tuvalu and Vanuatu).
Relief
In New Guinea and New Zealand also has mountain ranges. To the east of Australia, along the edge of the shelf stretches 2,300 km the Great Barrier Reef coral origin. Pacific islands and archipelagos are of volcanic or coral origin, some are active volcanoes.
